FlexConnect vs. Local Mode: Making the Right Choice for Cisco Wireless Deployments
Introduction:
In today’s digital world, wireless connectivity has become the backbone of modern organizations, enabling
- seamless communication
- data access
- and mobility.
Cisco, a leading networking solutions provider, offers a wide range of wireless solutions to meet the diverse needs of
- businesses
- institutions
- and enterprises.
When deploying Cisco wireless access points (APs), one crucial decision network administrators must make is choosing between two primary operational modes: FlexConnect and Local Mode. Each mode has its strengths and limitations, making the choice a critical aspect of designing an efficient and reliable wireless network.
Understanding FlexConnect and Local Mode:
Before delving into a detailed comparison, it is essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of FlexConnect and Local Mode.
FlexConnect Mode:
FlexConnect, also known as H-REAP (Hybrid Remote Edge Access Point), is designed to support remote branch deployments with limited or intermittent connectivity to the central controller.
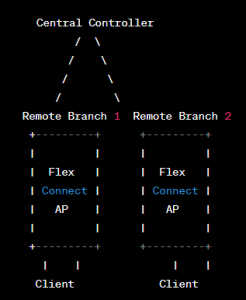
In FlexConnect mode, the access point can locally switch and authenticate client traffic, providing essential services even if the connection to the central controller is lost. This mode is especially beneficial for organizations with multiple remote sites that require local data traffic forwarding.
Local Mode:
On the other hand, Local Mode, as the name suggests, involves the access points directly connecting to the central controller for all data traffic processing and client authentication.
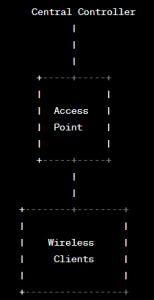
In this mode, APs act as a simple bridge, forwarding all traffic to the controller, which then handles the wireless client data.
Comparison:
Now that we have an overview of both FlexConnect and Local Mode, let’s delve into a detailed comparison between the two operational modes using a table to highlight the key features:
| Feature | FlexConnect Mode | Local Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Local Switching | Supported | Not Supported |
| Central Switching | Supported | Yes |
| Centralized | No (Limited) | Yes |
| Data Traffic | Local Bridging in Branch | Routed through Controller |
| Redundancy | Increased due to Local Switching | Reduced due to Central Mode |
| Traffic Management | Independent per Branch | Centralized |
| WAN Bandwidth | Optimized due to Local Switching | Consumed by Central Mode |
| Scalability | Suitable for Remote/Branch sites | Suitable for Centralized |
| Configuration | Separate configuration per branch | Unified configuration |
Flex Connect Mode: Advantages and Limitations
| Aspect | FlexConnect (H-REAP) | Local Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | – Supports remote branch deployments | – Simplified network design with direct AP-to-controller |
| – Limited or intermittent connectivity to the central controller | communication | |
| – Local switching and authentication for essential services | – Centralized control over all data traffic processing and | |
| during controller disconnection | client authentication | |
| – Suitable for organizations with multiple remote sites | – Allows for seamless roaming between access points | |
| requiring local data traffic forwarding | – Better performance as traffic is offloaded to the controller | |
| – Provides bandwidth savings by locally offloading traffic | – Easier management and troubleshooting with centralized | |
| instead of backhauling to the controller | control and monitoring | |
| – Reduces WAN link usage and latency | – Better suited for dense networks with high client density | |
| Limitations | – Limited centralized management, requiring separate configs | – Higher WAN bandwidth consumption due to centralization |
| for each branch location | – Dependency on the central controller, potential single | |
| – Reduced traffic redundancy compared to Local Mode | point of failure | |
| – Some advanced features may not be available | – Lack of local data traffic switching, making it less | |
| due to decentralized traffic management | suitable for sites with unstable connectivity | |
| – Complex management in large and distributed deployments |
Conclusion:
- Choosing the right operational mode for Cisco wireless access points is critical for network performance, scalability, and manageability.
- FlexConnect mode is ideal for businesses with remote and branch sites, offering local data traffic switching and reduced WAN bandwidth consumption.
- Local Mode is suitable for larger, centralized deployments like campuses and enterprises, providing comprehensive centralized management, enhanced traffic redundancy, and access to advanced features.
- The decision should consider the organization’s specific needs, network size, topology, data traffic patterns, security concerns, and available resources.
- A hybrid approach can be considered, combining both FlexConnect and Local Mode to leverage their strengths in different parts of the network.
- Properly implemented Cisco wireless deployment can deliver reliable, high-performance, and secure connectivity to meet modern digital demands.